
页面的滚动布局跟 CSS overflow 属性的设置息息相关,关系到某块溢出屏幕(容器)的元素部分能否正常滚动出现在视口中,或者相对于根元素定位的元素是否具有同步滚动的能力。overflow 从单个元素的视角理解不难,但是 overflow 的向上传播特性,使得它动辄影响页面布局,最后滚不滚得动就不好说了。
本文将用一个 demo 来观测 overflow、scroll 的具体表现。
overflow 相关属性
跟 overflow 相关的元素属性有 offsetHeight、clientHeight、 scrollHeight、scrollTop ,它们的计算方式为:
|
|
scrollHeight 相比 offsetHeight ,包含了子元素溢出的高度。
demo 中会观察每个元素的这几个值(最新版 Chrome 下测试 ),玄学还得用图和数据说话。
overflow demo
demo 最开始的代码如下:
|
|
当容器元素 container 没有设置 height 时,子元素 content 的高度 height: 500px 自动撑开父元素,container 高度(offsetHeight)此时为 content 的高度 + container水平 border 高度 = 520px
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| container | 520 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
父元素固定高度
在上面 demo 的基础上做些改动:
|
|
当设置了 container height: 300px; 后,content 高度溢出,因为父元素默认溢出不裁剪(overflow: visible),可以看到 content 溢出的部分覆盖了 container 的 bottom border,并且 content 溢出内容直接覆盖在了 container 相邻的 behind 元素上(见 overflow content),但 content 的 background 层叠等级小于 behind 元素的 background,所以 behind 元素的 background 在上面(玄不玄)。
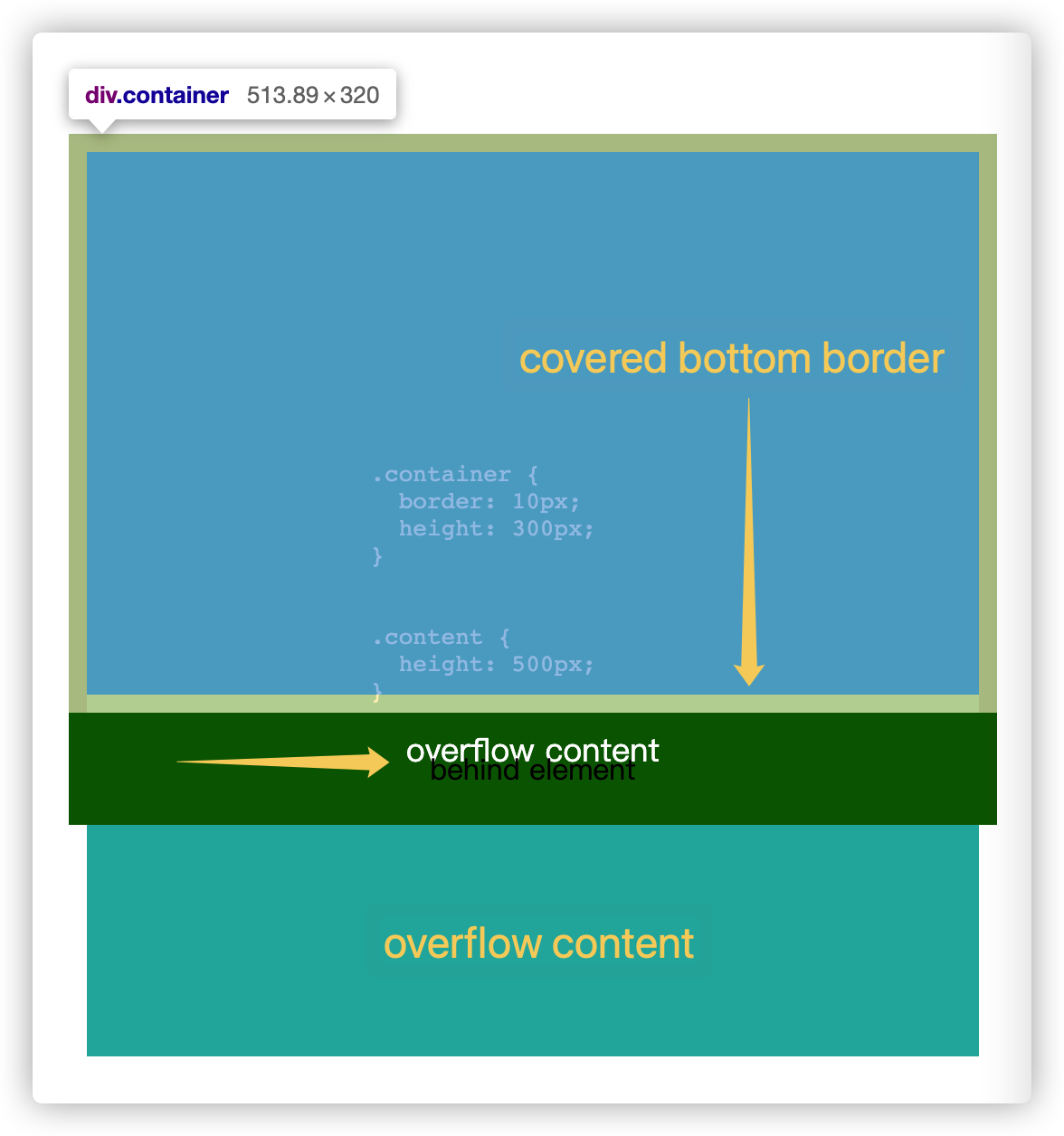
所以在默认情况下,溢出的内容不会影响正常的文档流,直接覆盖在父元素后面的元素上,可能影响正常页面信息的获取。
此时 container 和 content 元素的 scrollHeight 都为 500 px,因为父元素的 scrollHeight 会包含子元素的溢出部分,但不包含 border:
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| container | 320 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
父元素 overflow: auto
|
|
设置 container overflow: auto,让 content 溢出的内容隐藏,可视区域为父元素的 padding area(height 300 px),父元素开启滚动,可视区域出现垂直滚动条。
在 Mac 系统中,页面中出现的滚动条是悬浮覆盖在元素上,不占用滚动元素的宽度,即
scrollElement.offsetWidth中包含的滚动条宽度为 0。

当 container 滚动到底部,container.scrollTop 滚动的值为 content 顶部(不可见)到 container 可视区域 顶部的距离,content 的高度 500 px 在可视区域显示完 300 px 后,滚动到上面剩下的不可见区域高度为 200px,即等于 container 的滚动距离 scrollTop 200 px。cotainer 可视区域的高度为 clientHeight (不包括 border、溢出)300 px。
下面的等式可以用来判断 container 是否垂直滚动到最底部:
|
|
由于 content 不是可滚动元素(content 子元素没有溢出),所以在 container 滚动过程中,content.scrollTop 始终为 0。
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| container | 320 | 500 | 200 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
父元素 overflow: hidden
|
|
设置 container overflow: hidden 后,content 溢出的内容被裁剪隐藏,无法通过前端交互方式滚动元素,但仍然可以用 JS 控制 container 的滚动位置:
|
|

此时 content 溢出内容虽然被裁剪,但不影响 container.scrollHeight 的值(500 px),因为还存在溢出.
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| container | 320 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
页面容器布局
当创建页面容器布局时,容器元素 overflow 的设置会影响到顶级元素(html、body、root)的滚动区域。
假设页面窗口的视口高度为 400 px,root 根元素高度撑满视口高度(height: 100%):
|
|
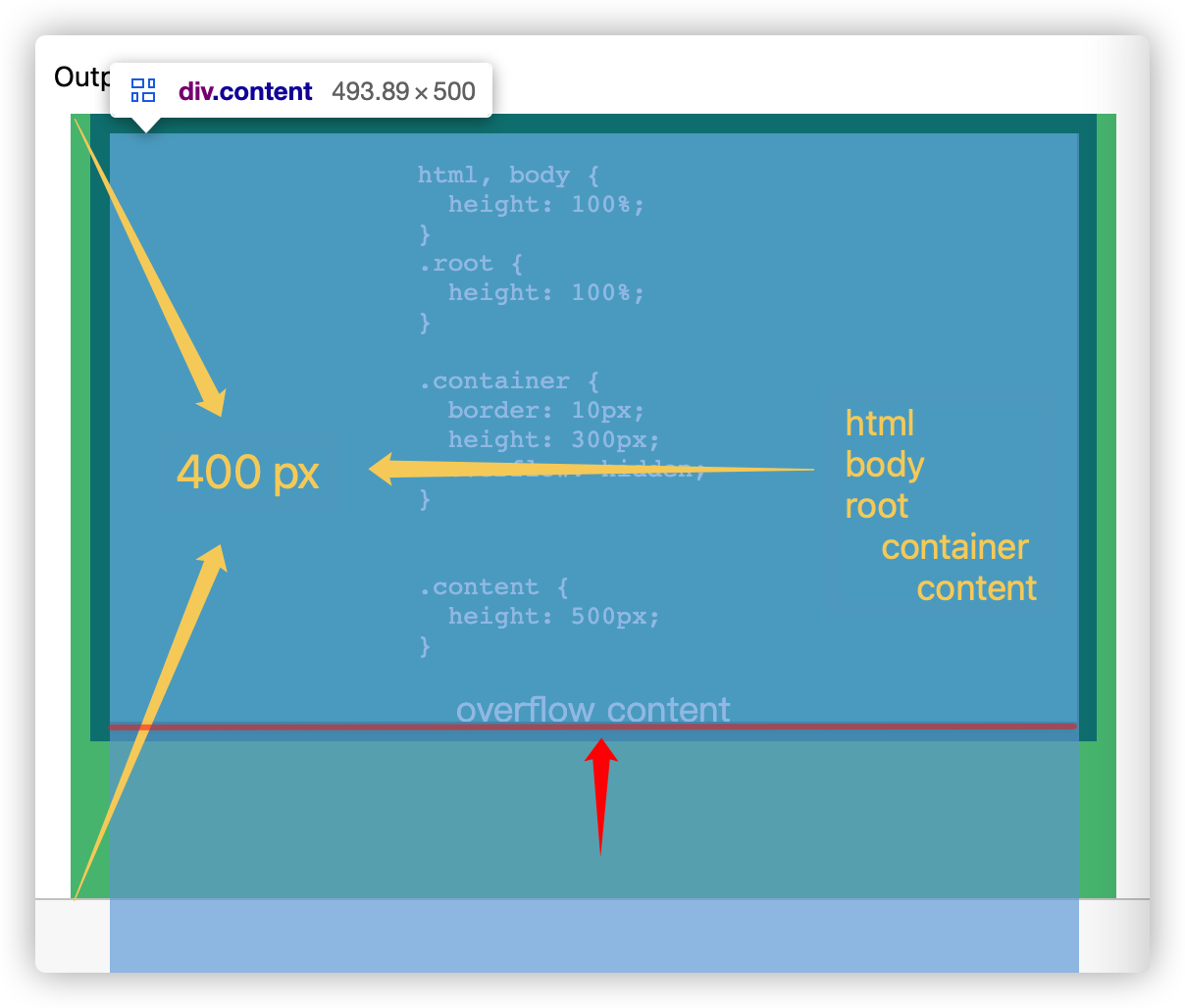
container 不管设置 overflow: auto 还是 overflow: hidden ,container 是否滚动不影响 container 本身的高度没有溢出 root 这个事实, 所以 root 的 scrollHeight 不包含 content 的溢出内容,还是等于自身高度( root.scrollHeight == root.offsetHeight == 400px)。
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| html | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| body | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| root | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| container | 300 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
同样地,container 设置 height: 100%; overflow: auto 后,即使从视觉上看整个页面都滚动了,但root.scrollHeight 还是 400 px,滚动只是发生在 container 元素上。
|
|

| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| html | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| body | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| root | 400 | 400 | 0 |
| container | 400 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
触发悬浮
如果有悬浮元素和触发元素是相对于 html 元素来定位偏移距离的(比如悬浮提示、下拉菜单),当悬浮元素初次出现在触发元素旁边后,触发元素在 container 中滚动时,假如没有动态的调整悬浮元素的相应偏移距离,悬浮层就会静止在最开始出现的位置,没有跟随触发元素滚动,造成视觉上的分离,显得突兀。(当然如果设计成滚动时关闭悬浮元素,那自然就没有这个问题)
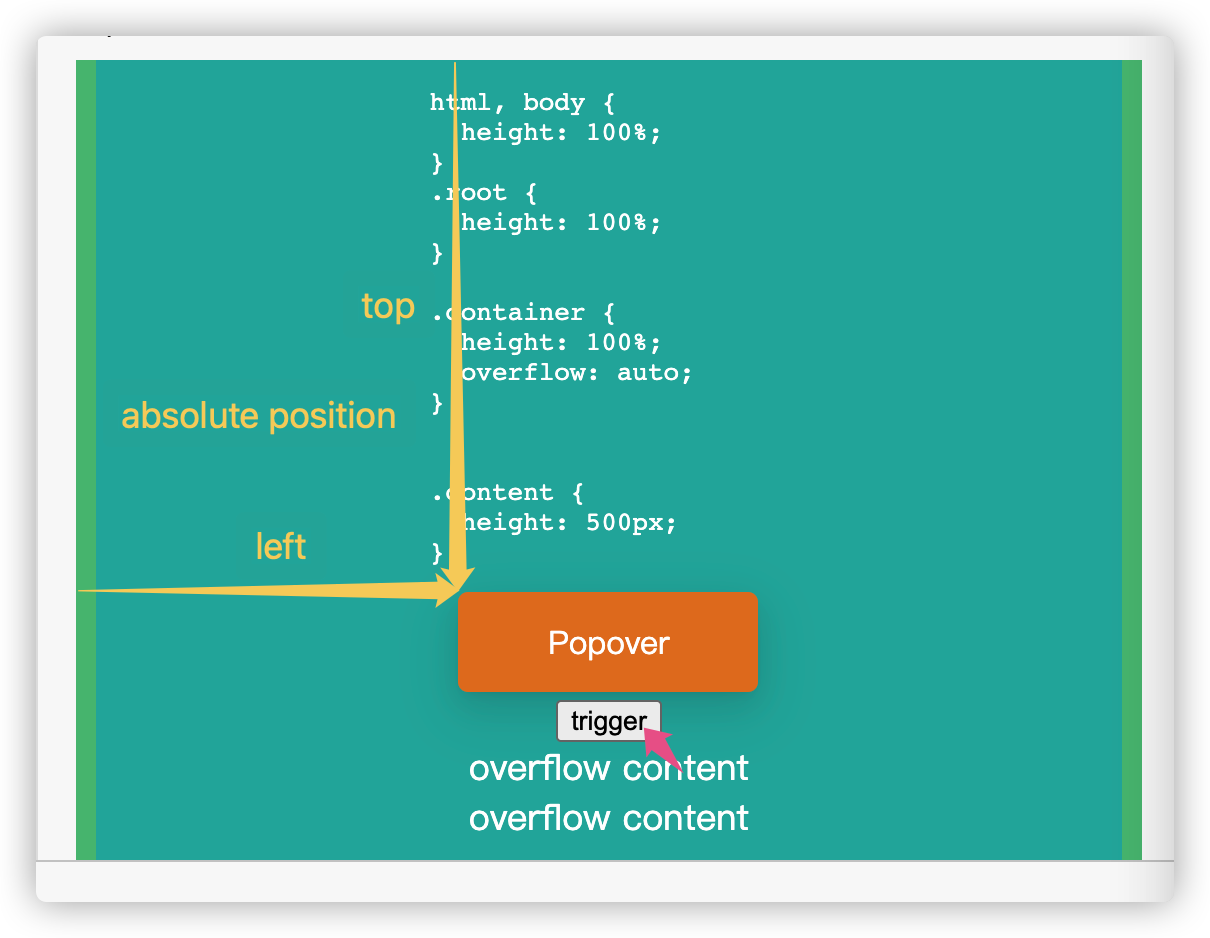
上图中,当指针悬浮在触发元素 trigger 元素上时,会计算 trigger 在视口中的位置和滚动距离:
|
|
悬浮元素 Popover 根据 triggerOffsetX、triggerOffsetY 和自身尺寸计算相对于 html 的偏移距离:
|
|
点 (PopoverOffsetLeft, PopoverOffsetTop) 就是 Popover 的左上角坐标:
|
|
当 trigger 在 container 中滚动时,Popover 还是悬浮在原来那个位置静止,滚动并没有作用在 Popover 上(Popover 相对于 body ),trigger 和 Popover 出现分离:
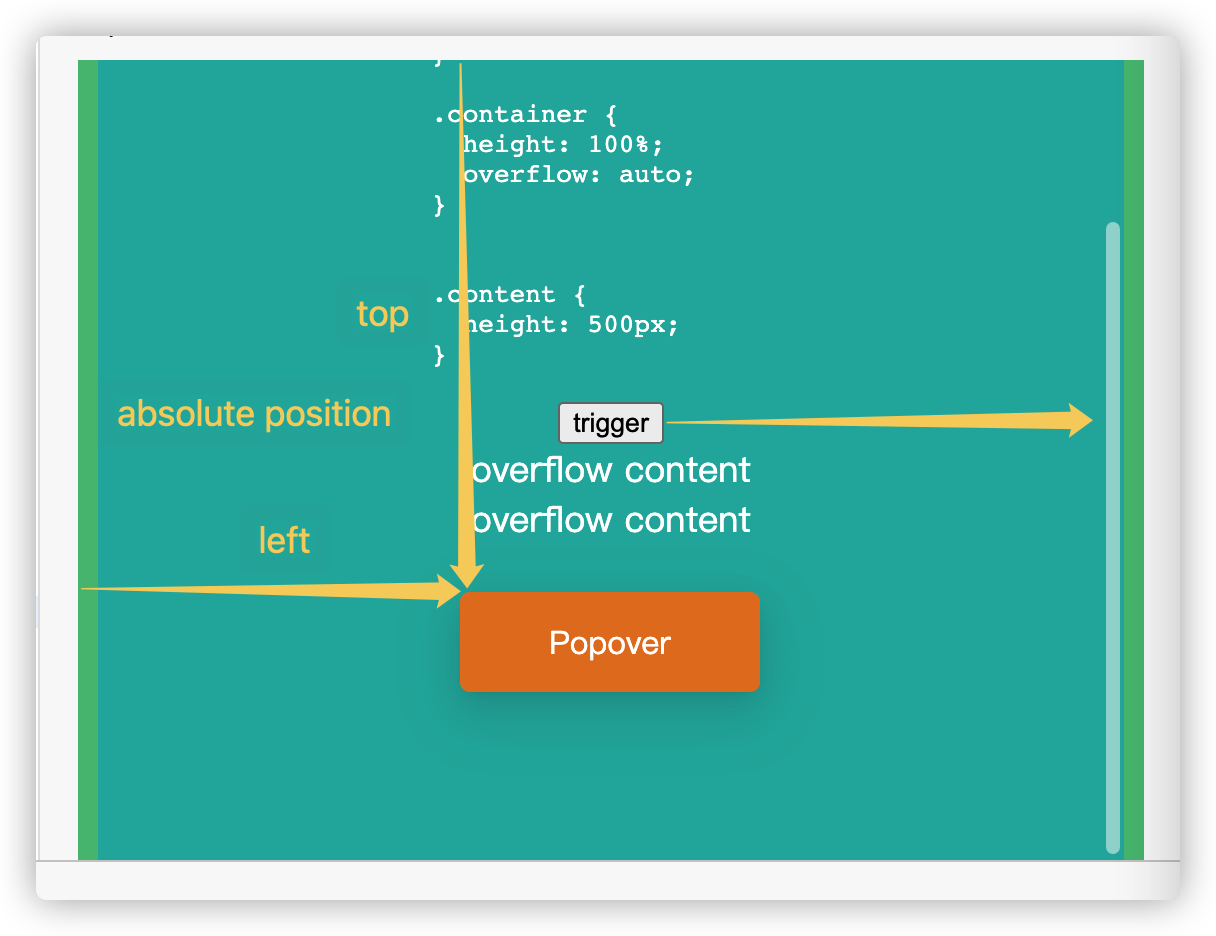
html 溢出
|
|
container 删除 overflow:auto 后,溢出的 content 超出了 cotainer、root、body、html 对应的视口高度(height: 100%),最终在 html 元素上触发了溢出滚动,html 作为最终的滚动区域,滚动区域高度跟 content 的高度一致,所以 Popover 相对于 html 元素在滚动区域偏移定位到 trigger 旁边后,Popover 会跟随 trigger 在滚动区域滚动,保持相对静止:
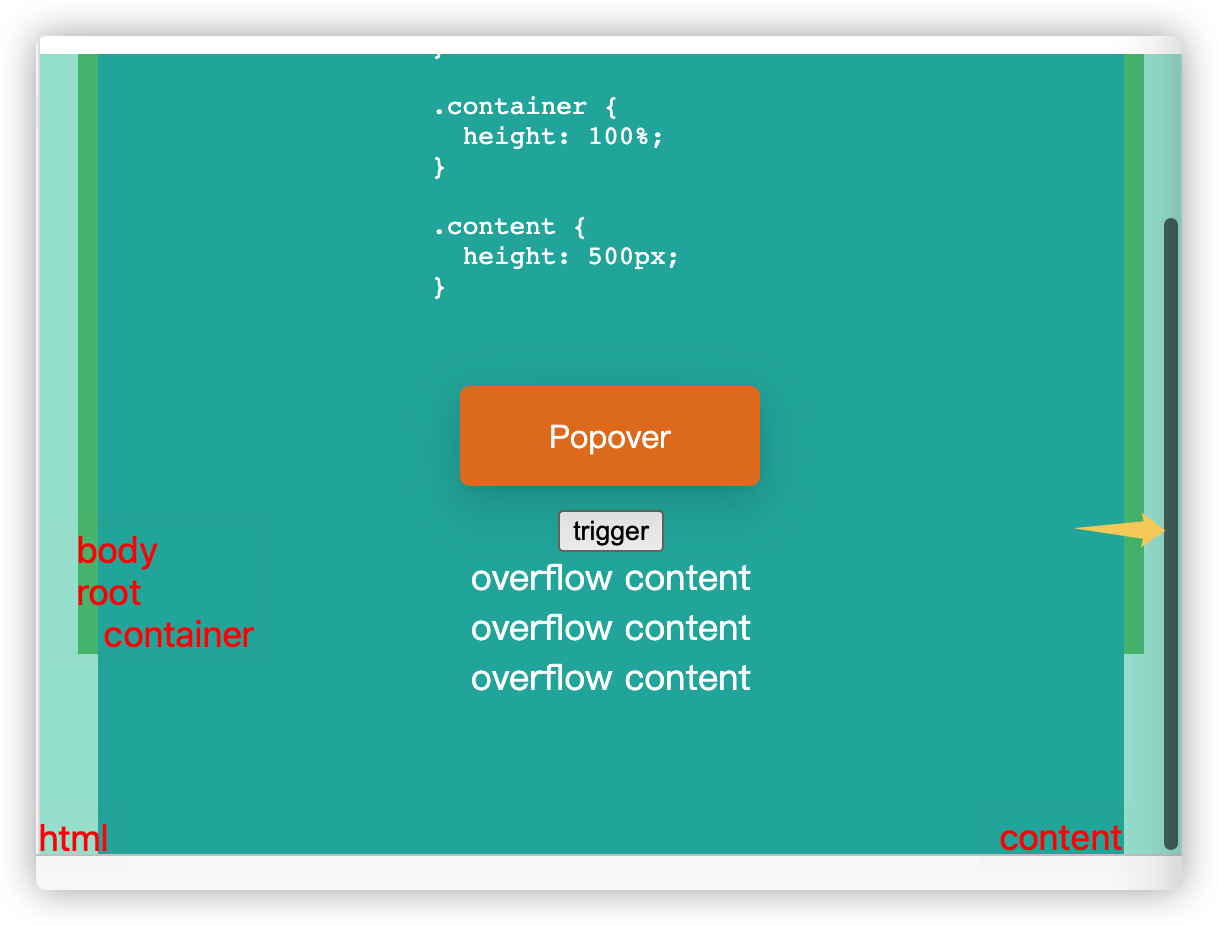
滚动到底部后,html.scrollTop 正好是 content.offsetHeight 和 html.offsetHeight 的高度差 100 px。
| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| html | 400 | 500 | 100 |
| body | 400 | 500 | 0 |
| root | 400 | 500 | 0 |
| container | 400 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
html 无固定高度
如果把 html 的 height: 100% 去掉:
|
|
此时 html 不再限制为视口的高度, body, root, container { height: 100% } 的高度百分比没有了相对计算的值,退化为 heigth: auto,由子元素内容高度决定, content 的固定高度层层向上撑开了 html 的高度,html 的高度此时跟 content 的高度一致,html 下没有发生高度溢出,视口成为滚动区域,但是可以在 html 中控制滚动。

| 元素/高度(px) | offsetHeight | scrollHeight | scrollTop |
|---|---|---|---|
| html | 500 | 500 | 100 |
| body | 500 | 500 | 0 |
| root | 500 | 500 | 0 |
| container | 500 | 500 | 0 |
| content | 500 | 500 | 0 |
设置 html { min-height: 100%; } 、html { min-height: 100vh; } 也是同样的效果,只要 html 的高度不固定,就会被子元素高度撑开。
结论
所以如果要避免上面悬浮元素不跟随滚动的问题,不能在某个容器元素上设置 overflow: auto、overflow: hidden ,需要让子元素溢出屏幕高度的部分向上传播,撑开 html、body 的高度,让 html、body 的滚动区域高度跟 content(长元素)高度一致,即悬浮元素跟触发元素的滚动背景重叠,保证同步滚动。
其实让悬浮元素跟随滚动还有另一种思路, html、body 作为悬浮元素定位的参考元素只是通用方案,悬浮元素也可以直接挂载到长元素下,跟触发元素处于同一滚动区域,自然就能在滚动时保持相对静止。通常组件库中的悬浮层都会提供自定义挂载点的 API,就是用来绕过 body 没撑开或不滚动的布局,见 Ant Design Select 组件 getPopupContainer() prop。
总结
本文重温了 CSS overflow 的基础特性,和与其相关联的元素高度属性,并通过 demo 观测 overflow 的各个值是如何影响元素高度、页面布局的,探索如何解决悬浮元素滚动分离的问题。以后在遇到滚动相关问题时,可以利用 overflow、scrollTop 定位滚动区域,弄清楚是哪个子元素在父元素里溢出了。
CSS 真是越学越玄,很多情况都需要依靠具体表现和数据来推断浏览器的页面渲染机制,玄学还得靠实验观测👁
参考
Measuring Element Dimension and Location with CSSOM in Windows Internet Explorer 9